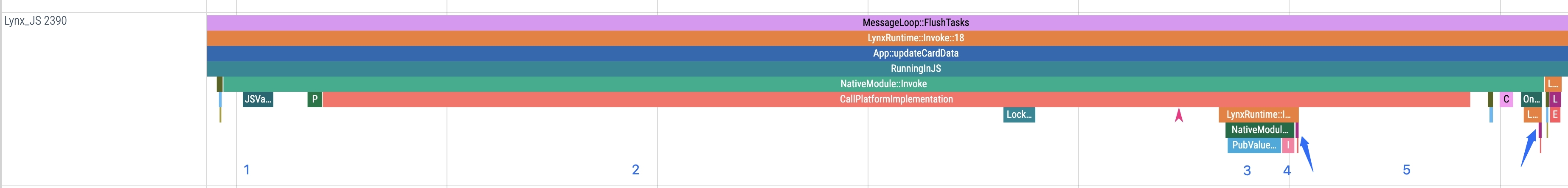
NativeModule Invocation
NativeModule is the core communication bridge between JavaScript and native applications. By invoking a NativeModule, Lynx frontend pages can access and control native capabilities. This document together with code examples, details the invocation and execution flow of NativeModule within Trace.
Deep analysis with Trace
Since Lynx 3.2, the Trace page includes a NativeModule Track that aggregates all NativeModule invocations. Each item’s length reflects the overall duration from request initiation to completion.
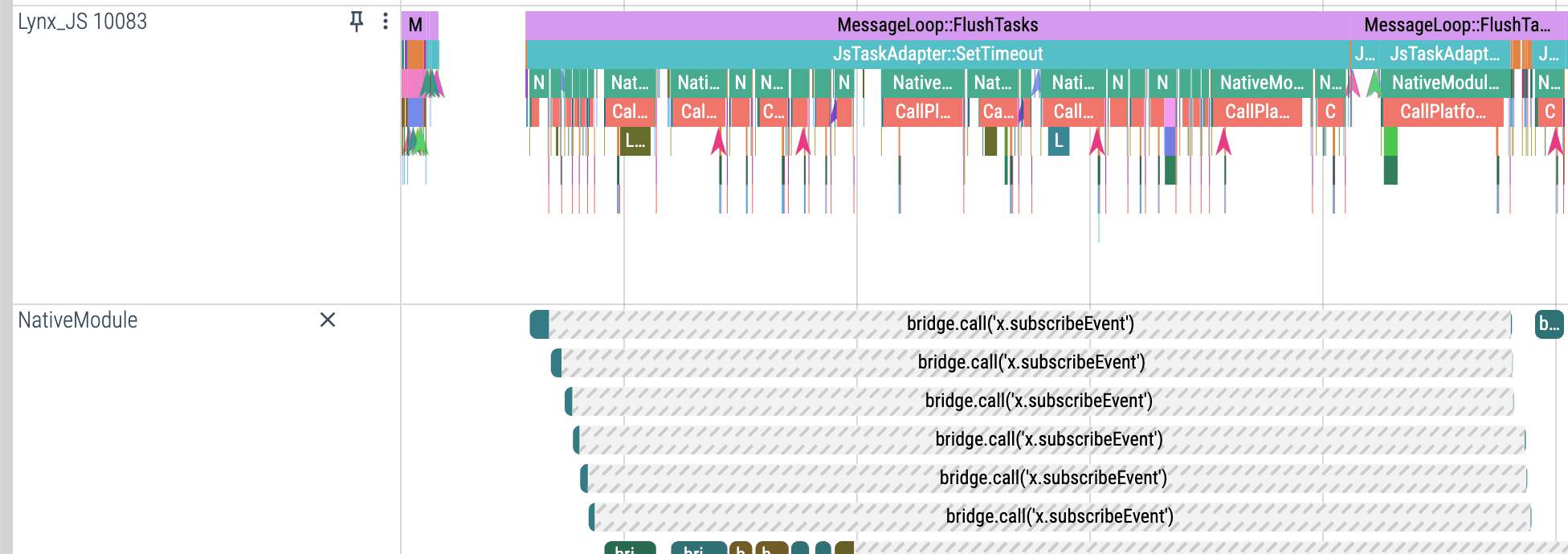
Basic display: click an item in the NativeModule Track to view a color-coded breakdown of rough durations for each stage of the invocation.
Details panel: shows the method name, input parameters, and precise per-stage durations (including parameter conversion, platform logic, thread switches, and other key nodes).

Breakdown of NativeModule invocation details
Below we use a frontend NativeModule call as an example to describe execution timing in Trace.
Example code
Trace execution analysis
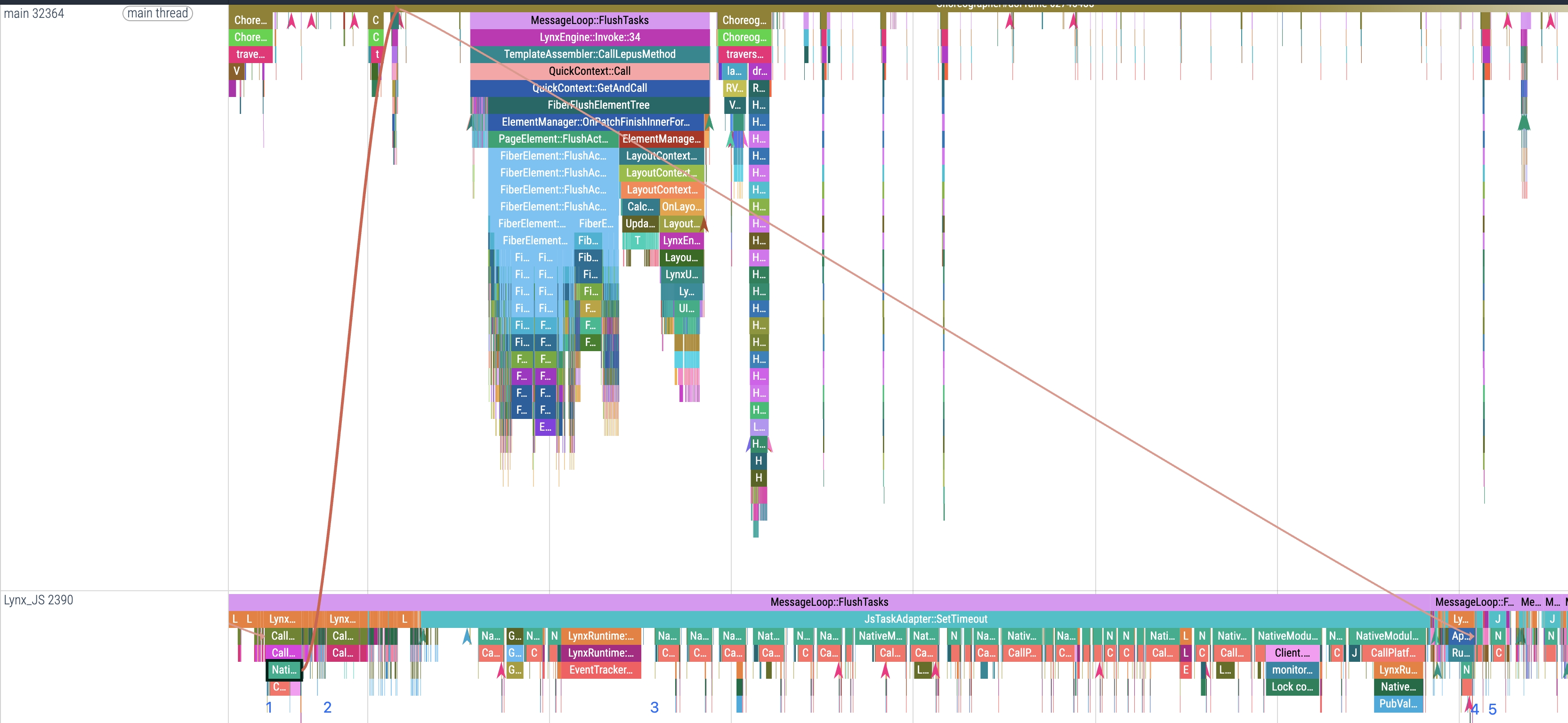
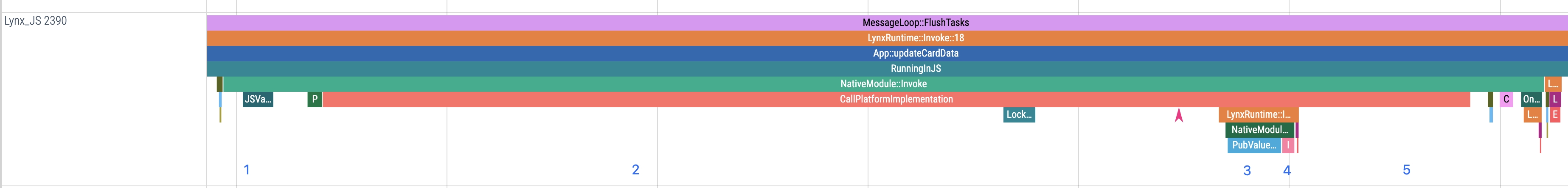
A NativeModule call can be divided into five main stages:
1. Parameter conversion
This stage corresponds to JSValueToPubValue in Trace, where JS data (lines 4–7 in the code sample) is converted into native types.
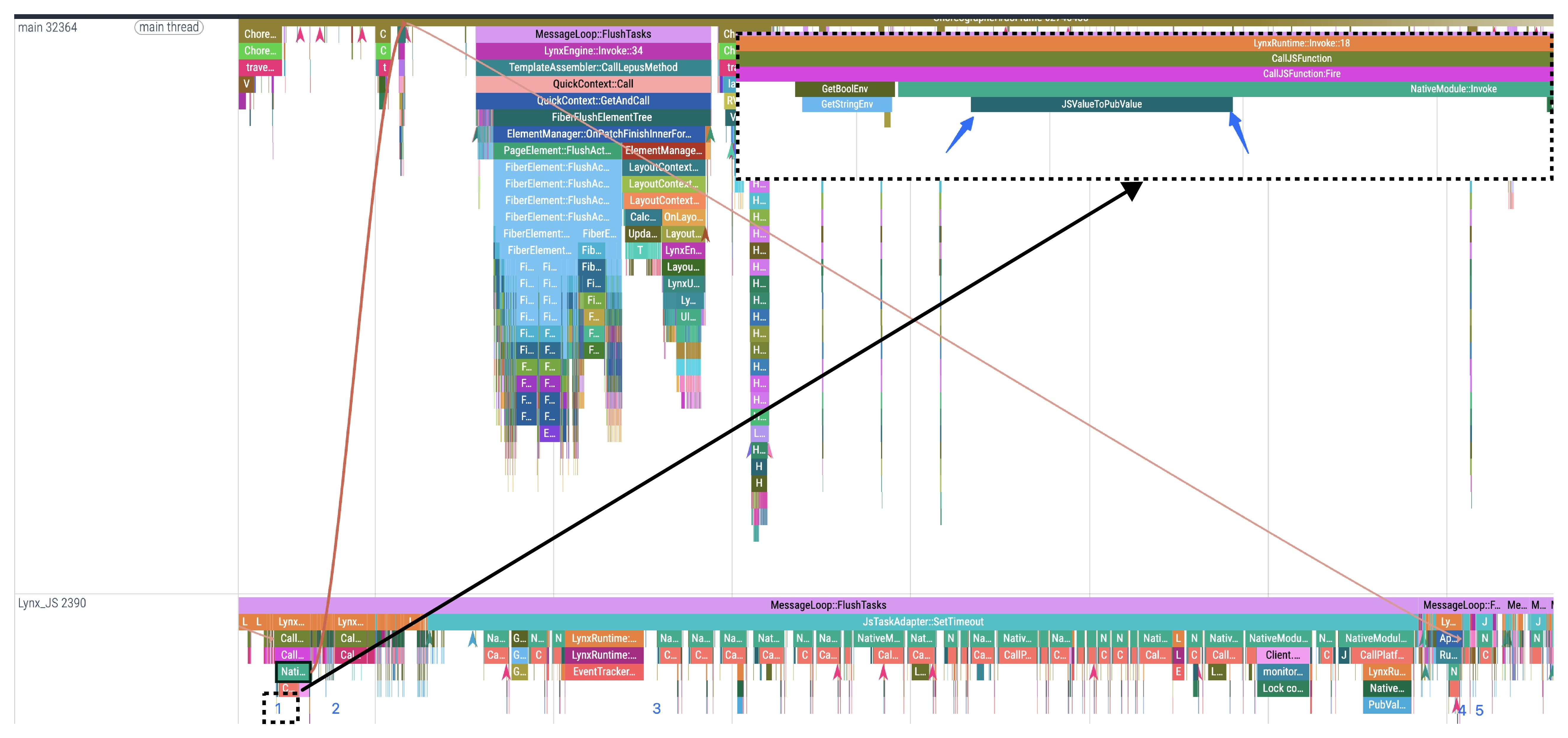
2. Platform-layer implementation
This stage corresponds to the time period in the Trace from the start of CallPlatformImplementation to NativeModule::PlatformCallbackStart, where the native method executes the specific functionality and returns platform-layer data.
Among them, the CallPlatformImplemention occurs on the background thread, while the logic between the CallPlatformImplementation event and NativeModule::PlatformCallbackStart usually runs on other threads.
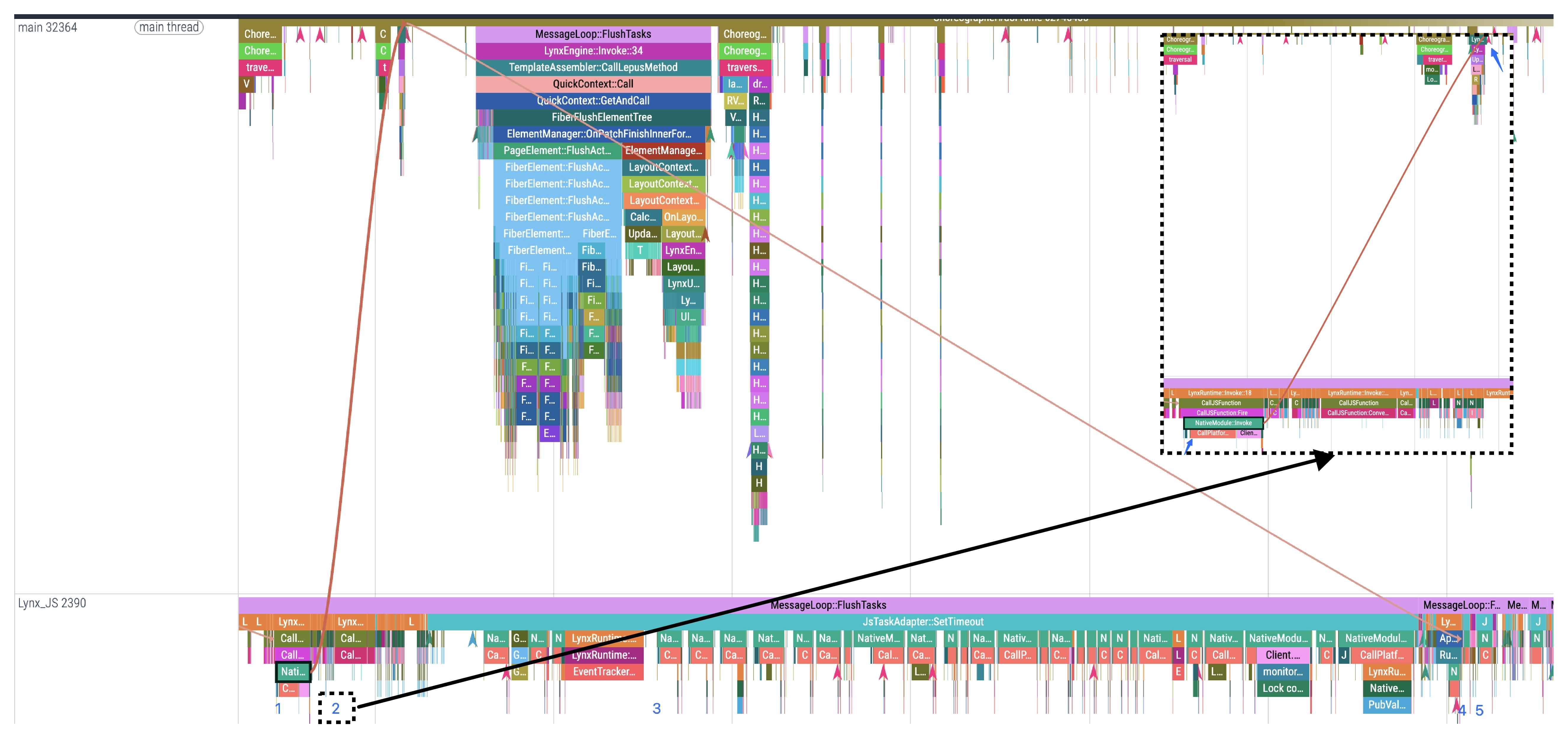
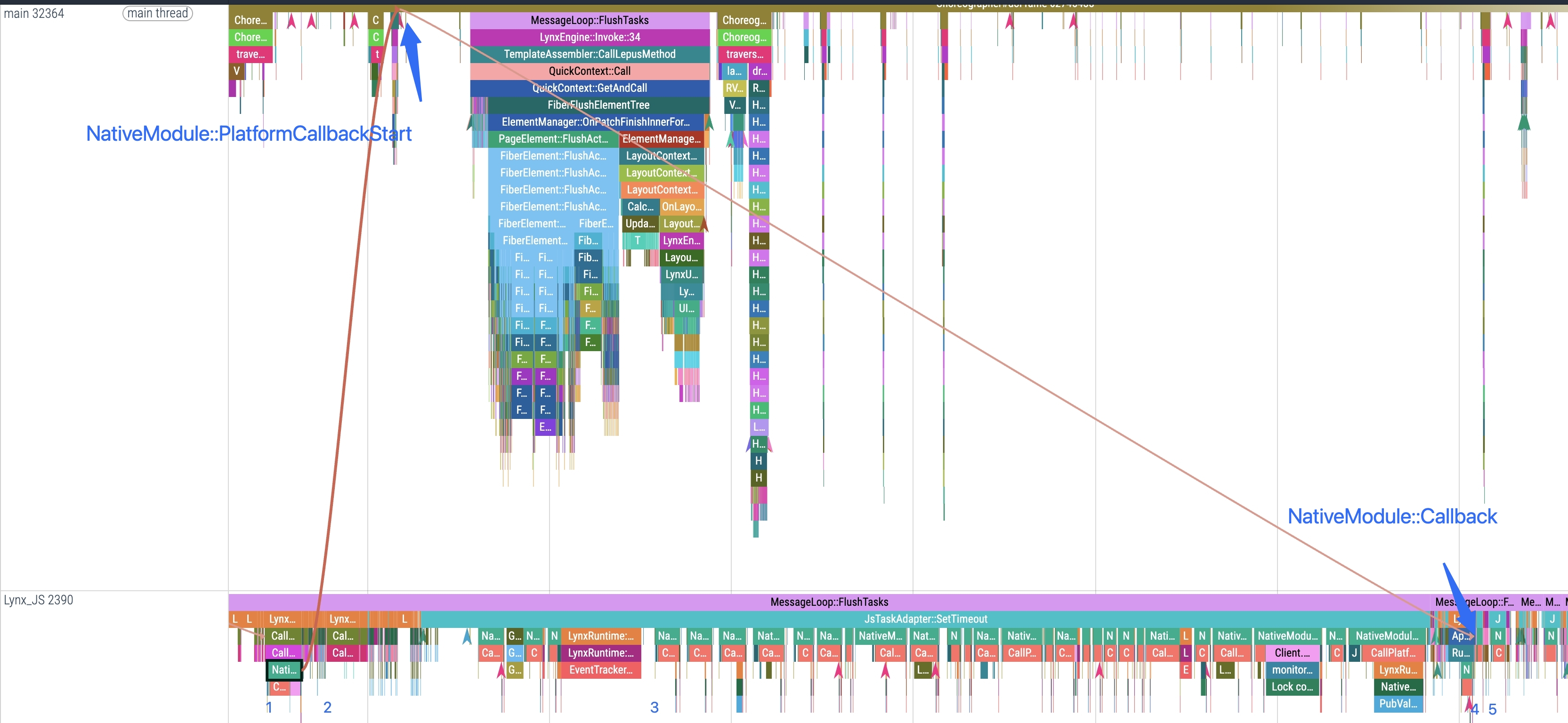
3. Waiting for the background thread to execute the callback
This stage corresponds to NativeModule::PlatformCallbackStart and NativeModule::Callback in Trace.
4. Result conversion
This stage corresponds to PubValueToJSValue in Trace, where platform-layer return data is converted into JS arguments.
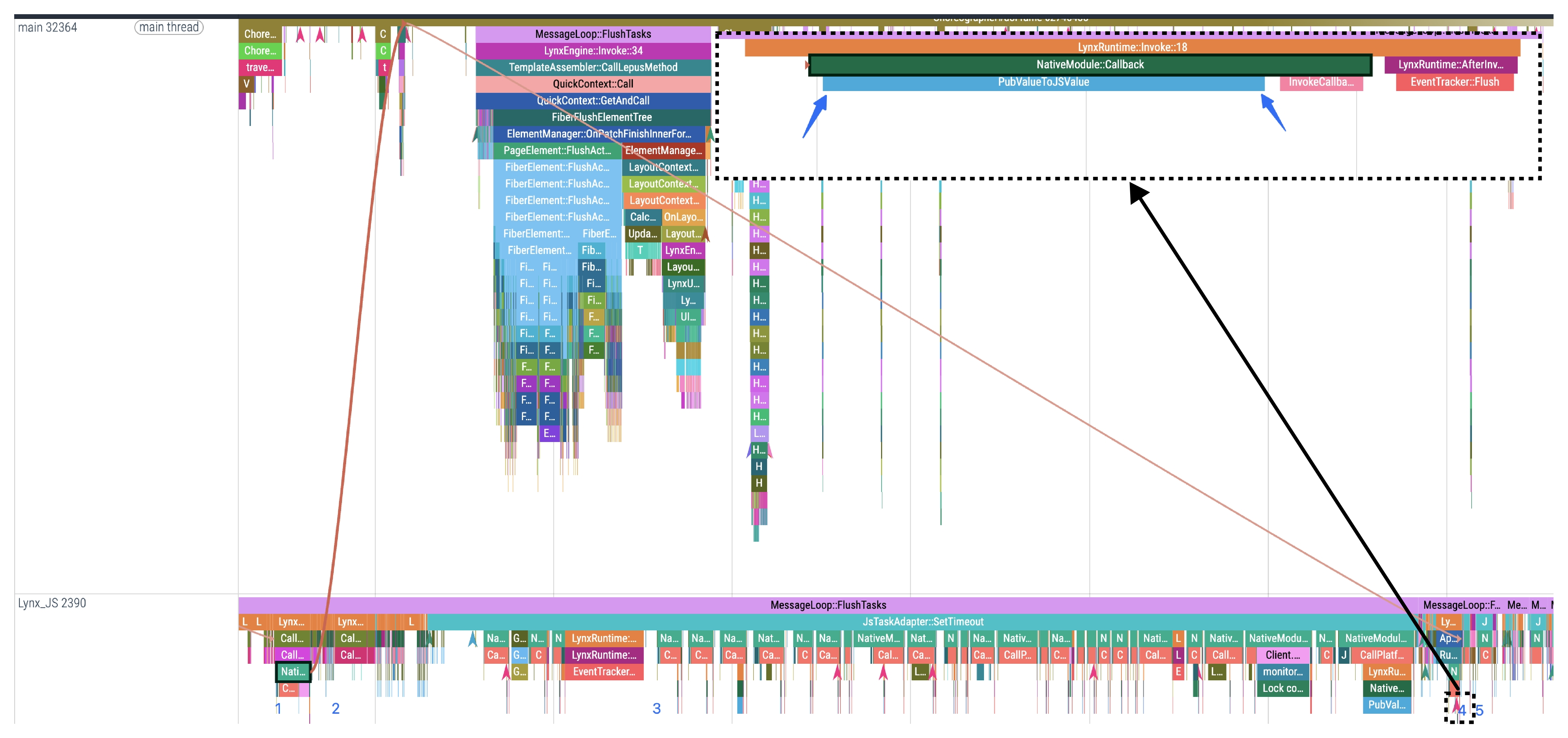
5. Callback execution
This stage corresponds to InvokeCallback in Trace, which executes JS code logic (line 10 in the sample).

Special NativeModule calls
Currently, JSB SDKs in the company return results via callbacks. Some NativeModule implementations return results directly to the Lynx SDK via callbacks on the background thread. Callback execution is not necessarily limited to the main thread—any thread may invoke and execute callback-related logic.
Example code
Trace execution analysis
These special NativeModule calls can be divided into five main stages.
1. Parameter conversion
This stage corresponds to JSValueToPubValue in Trace, where JS data (lines 4–6 in the sample) is converted into native types.
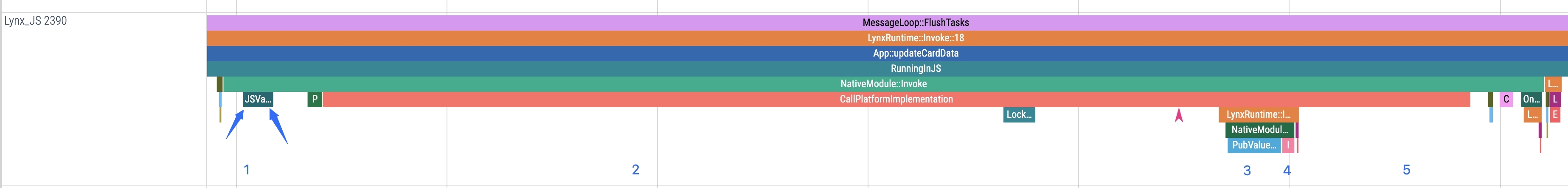
2. Platform-layer implementation
This stage corresponds to the time period in the Trace from CallPlatformImplementation to the start of NativeModule::Callback, where the native method executes the specific functionality and returns platform-layer data.
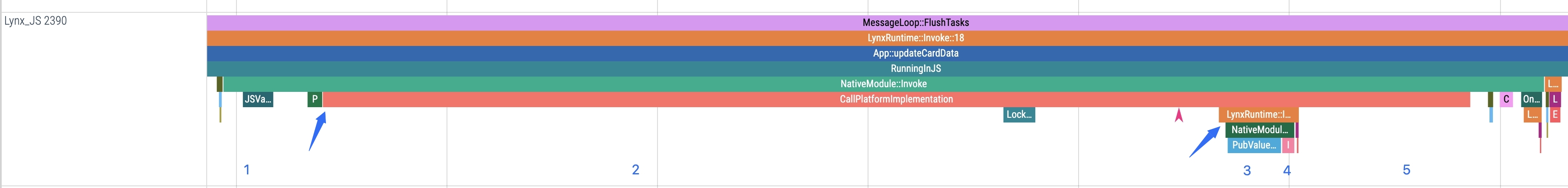
3. Result conversion
This stage corresponds to PubValueToJSValue in Trace, where platform-layer return data is converted into JS arguments.
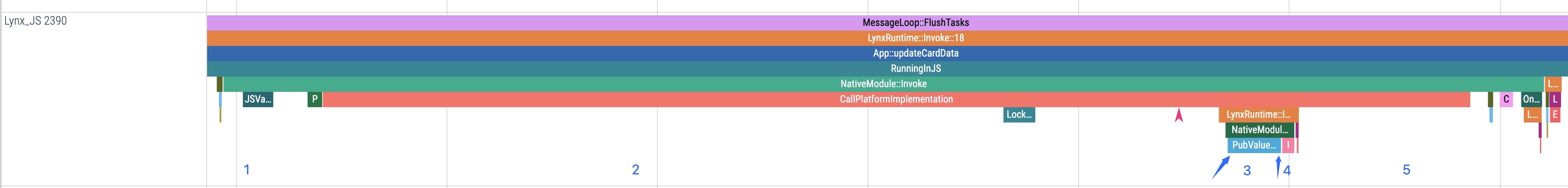
4. Callback execution
This stage corresponds to InvokeCallback in Trace, which executes JS code logic (line 9 in the sample).
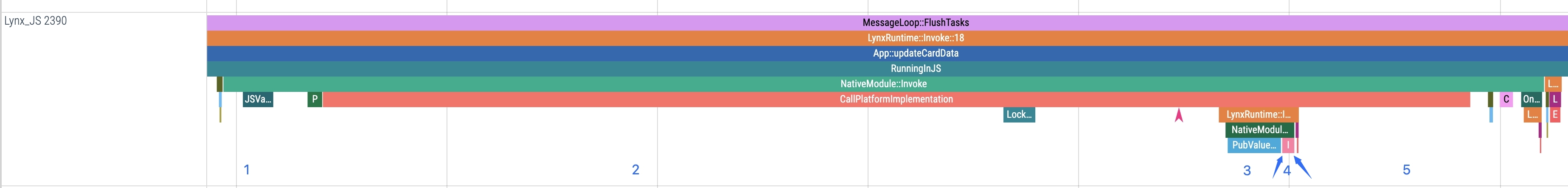
5. Cleanup
This stage corresponds to the time period in the Trace from the end of InvokeCallback to the end of NativeModule::Invoke, where platform-layer cleanup is performed and external registrants are notified that the NativeModule call has completed.